What is APAC and EMEA?
APAC and EMEA are acronyms of regions that are grouped together for business or government purposes. Companies need to understand what makes each unique to succeed in these regions. In this article will look at APAC and EMEA, the countries they include, and some interesting facts about them.
What is APAC?
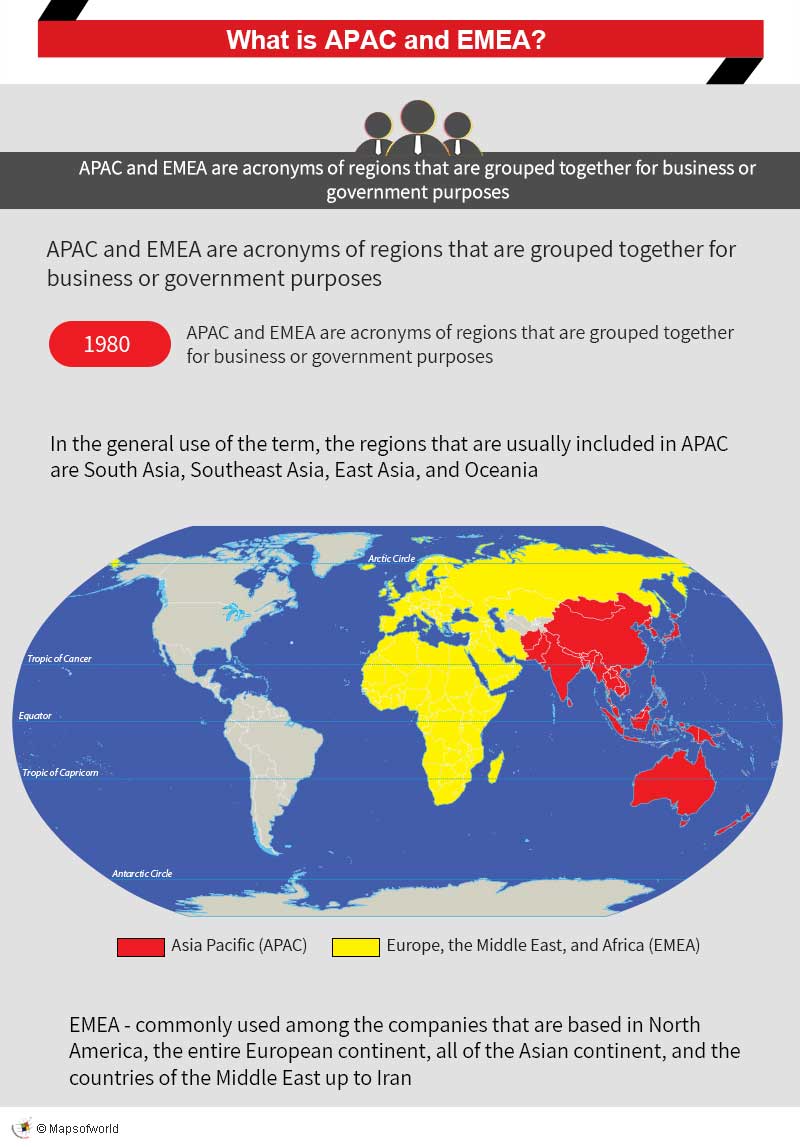
The term Asia Pacific came into use in the 1980s concerning finance and politics. However, there is no single definition of the term, as the regions included in APAC may change, according to the context for which the term is being used. The areas that are usually included in APAC are South Asia, Southeast Asia, East Asia, and Oceania.
APAC is a leader in digital innovation, especially in mobile technology and e-commerce. Major tech companies like Alibaba, Tencent, Samsung, and Sony are based in this region.
Countries in APAC
The Asia-Pacific region comprises the following countries:
- East Asia: China, Japan, South Korea, North Korea, and Taiwan.
- Southeast Asia: Indonesia, Thailand, Vietnam, Malaysia, Philippines, Singapore, Myanmar (Burma), Cambodia, Laos, Brunei, and Timor-Leste.
- South Asia: India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Nepal, Bhutan, and Maldives.
- Oceania: Australia, New Zealand, Papua New Guinea, Fiji, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Samoa, Kiribati, Tonga, Micronesia, Marshall Islands, Palau, Tuvalu, and Nauru.
Interesting Facts about APAC
- APAC is one of the fastest-growing economic regions in the world. Countries like China, India, and Southeast Asian nations, have shown significant economic growth, contributing substantially to the global economy.
- The region is experiencing an e-commerce boom, with online retail sales growing exponentially. China is the largest e-commerce market globally, and other countries like India and Indonesia are also seeing rapid growth in online shopping.
- Fast urban growth in APAC is opening up new business opportunities, especially in building infrastructure, real estate, and urban services. Big cities like Tokyo, Shanghai, and Mumbai are important economic centers in the region.
What is EMEA?
EMEA, which is a business term, is commonly used among companies that are based in North America. This is a much more straightforward definition and includes the entire European continent, all of the Asian continent, and the countries of the Middle East up to Iran. Russia, both the European and Asian parts, are also included in EMEA. However, usually excluded from EMEA are the overseas territories of any EMEA countries.
As it is a business term, it is used by companies to specify their divisions that are operating in Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. These divisions are geared to meet the needs of the specific region and are usually operated by a separate CEO or Business Head. Businesses treat EMEA as a single region for operations, marketing, and strategy because it has diverse economies and big market opportunities.
Countries in EMEA
Here’s a list of countries typically included in EMEA:
- Europe: United Kingdom, Germany, France, Italy, Spain, Russia, Turkey, Poland, Netherlands, Belgium, Switzerland, Sweden, Austria, Norway, Denmark, Finland, Greece, Portugal, Ireland, Czech Republic, Romania, Hungary, Slovakia, Croatia, Bulgaria, Serbia, Ukraine, Belarus, Slovenia, Lithuania, Latvia, Estonia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Albania, Montenegro, Macedonia, Kosovo, Moldova, Cyprus, Malta, Iceland, Luxembourg, Andorra, Liechtenstein, Monaco, San Marino, Vatican City.
- Middle East: Saudi Arabia, Iran, United Arab Emirates (UAE), Iraq, Israel, Qatar, Kuwait, Oman, Bahrain, Jordan, Lebanon, Syria, Yemen, Palestine, Cyprus (parts of both Europe and the Middle East), Turkey (parts of both Europe and the Middle East).
- Africa: Nigeria, South Africa, Egypt, Algeria, Morocco, Ethiopia, Kenya, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Ghana, Mozambique, Ivory Coast (Côte d’Ivoire), Cameroon, Angola, Niger, Burkina Faso, Mali, Malawi, Zambia, Somalia, Senegal, Chad, Zimbabwe, Rwanda, Tunisia, Guinea, Benin, Burundi, Togo, Sierra Leone, Libya, Congo (Democratic Republic), Central African Republic, Mauritania, Eritrea, Namibia, Gambia, Botswana, Gabon, Lesotho, Equatorial Guinea, Mauritius, Eswatini (Swaziland), Djibouti, Comoros, and Seychelles.
Interesting Facts about EMEA
Here are some intriguing facts about this expansive and dynamic area:
- The region’s location is important for trade and shipping. Major ports like Rotterdam, Hamburg, and Dubai are crucial for global trade. They act like gateways that connect Europe, the Middle East, and Africa with the rest of the world.
- The European Union (EU) imposes strict laws on protecting data (GDPR), maintaining environmental cleanliness, and ensuring fair treatment of consumers. Businesses must carefully follow these rules.
- In EMEA, there’s a big focus on being sustainable and doing good for society (CSR- Corporate Social Responsibility). European countries, especially, are leading the way in using renewable energy, farming in eco-friendly ways, and creating green technologies.
Related Links
- What European Countries are Not Members of the EU?
- How Many Countries are Members of the European Union?


